Aluminum: The Lightweight, High-Performance Metal Revolutionizing Jewelry Design
Aluminum is a lightweight, soft, and highly malleable silver-white metallic element that’s as versatile as it is abundant. As the most common metal element in the Earth’s crust, aluminum is a major player across various industries. The extraction of aluminum typically involves the Hall-Héroult electrolytic process, where aluminum oxide is split into pure aluminum and oxygen through electrolysis.
The real magic happens when aluminum is combined with other elements to enhance its strength and corrosion resistance, making it not only tough but also incredibly durable. This adaptability is why aluminum is widely used in everything from aerospace engineering to automotive applications. But beyond its industrial strength, aluminum has another trick up its sleeve—it’s an environmentally friendly material that can be endlessly recycled without losing its original properties.
In the custom jewelry industry, these features make aluminum a top choice for crafting modern, sustainable pieces. Its lightweight nature, combined with excellent ductility and malleability, allows for creative designs that are comfortable to wear and easy to shape. Plus, its cost-effectiveness means that high-quality aluminum jewelry can be both affordable and eye-catching, making it the perfect metal for fashion-forward jewelry enthusiasts who want it all: beauty, durability, and a low environmental impact.
With aluminum, jewelry designers can push the boundaries of traditional metalworking, creating everything from delicate, intricate patterns to bold, statement-making pieces—all while staying green. This makes aluminum not just a metal of choice, but a movement towards a more innovative and sustainable future in jewelry design.
The Many Uses of Aluminum: A Metal That Does It All
Aluminum is a truly versatile material, and its lightweight structure and impressive strength make it the material of choice for a wide range of industries. Let’s take a look at some of the areas where aluminum is used:
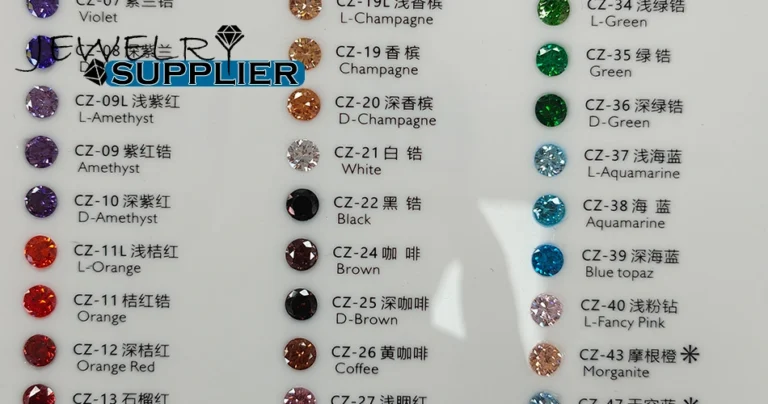
Data sheet of commonly used raw materials for jewelry
1. Transportation: In the automotive, aerospace, and high-speed rail industries, aluminum is prized for its combination of lightness and high strength. Using aluminum in cars, planes, and trains helps reduce overall weight, which reduces fuel consumption and increases energy efficiency. No wonder aluminum has become a staple in cutting-edge transportation technology!
2. Construction: Aluminum is a favorite in building construction for its excellent corrosion resistance and modern aesthetic appeal. It is widely used in doors, windows, roofs, and even decorative elements. Whether it’s a sleek skyscraper exterior or a durable window frame, aluminum adds style and functionality to building designs.
3. Electrical Industry: Aluminum has excellent electrical conductivity and is often the metal of choice for cables, transformers, and other electrical components. It ensures efficient power transmission while keeping weight low compared to other metals, making it both economical and energy-efficient.
4. Industrial Applications: Aluminum is widely used in machinery, piping systems, tools, and heat exchangers. Its high thermal conductivity and excellent machinability allow it to precisely manufacture complex parts, which is why it is indispensable in the manufacture of various mechanical components.
5. Aerospace Industry: In the aviation field, aluminum is an indispensable material for manufacturing aircraft skins, fuel tanks, and structural components. Its lightweight properties not only improve fuel efficiency, but also enhance durability and safety, making it a top material for the sky.
From reducing transportation fuel costs to powering the grid and shaping the skyline, aluminum continues to prove itself as a versatile and high-performance metal. It is everywhere, it can do everything, and it has style.
Aluminum Refining
The aluminum refining process is a complex and delicate process, mainly using the Hall-Heroult electrolysis method. In this process, alumina is used as the raw material, and under the influence of cryolite as a flux, alumina is electrolytically decomposed into aluminum and oxygen. The aluminum refining process requires high temperatures, resulting in the consumption of a large amount of energy and raw materials.
As technology continues to improve, aluminum refining processes are also being optimized. Innovations include the use of new electrolytic cells, the development of energy-saving technologies, and the improvement of raw material utilization, all of which are aimed at reducing production costs and minimizing environmental pollution. Innovation and development of aluminum refining technology are essential to the sustainable development of the aluminum industry.
Continuous improvements in aluminum refining processes not only improve efficiency, but also support the industry’s commitment to environmentally friendly practices, making aluminum a responsible choice for a wide range of applications.
Environmental Benefits of Aluminum
Aluminum is a metal known for its excellent environmental performance. Its recycling rate is remarkably high, with the energy consumption and emissions associated with recycled aluminum being significantly lower than those of primary aluminum production. This characteristic greatly contributes to energy conservation and environmental protection.
Additionally, aluminum does not release harmful substances during its use, making it safe for both the environment and human health. Its lightweight properties help reduce the overall weight of products, which in turn decreases energy consumption and emissions during transportation. Overall, aluminum stands out as a sustainable choice, promoting eco-friendly practices while maintaining high performance in various applications.
Characteristics of Aluminum
Aluminum is a versatile material known for its lightweight nature, high electrical and thermal conductivity, excellent ductility, and plasticity, making it widely used in industrial production. The lightweight properties of aluminum make it an ideal choice for manufacturing lightweight products, such as automobiles and airplanes. Its high electrical conductivity ensures its significant application in power transmission and electronic devices. Additionally, aluminum’s thermal conductivity makes it a preferred material for manufacturing heat exchangers and radiators.
The ductility and plasticity of aluminum facilitate easy processing and shaping, allowing for a variety of products in different shapes and specifications. Moreover, aluminum also boasts excellent corrosion resistance and aesthetic appeal, which further enhances its use in architectural decoration and everyday items. Overall, aluminum’s unique characteristics make it a go-to material across multiple industries.
Elements in Aluminum
Aluminum is a pure element, but in practical applications, it is usually found in alloy form. Aluminum alloys are made by adding other elements, such as copper, manganese, silicon, magnesium, and zinc, to enhance the mechanical properties and corrosion resistance of aluminum. The addition of different elements gives aluminum alloys unique properties, making them suitable for a variety of applications.
1. Copper (Cu): Increases the strength and hardness of aluminum alloys, making them ideal for manufacturing high-strength components in aerospace equipment.
2. Magnesium (Mg): Improves the tensile strength and yield strength of aluminum alloys and is often used in lightweight components.
3. Silicon (Si): Improves the casting properties of the alloy and is often used to cast aluminum alloys.
4. Manganese (Mn): Used to increase the strength of the alloy while improving corrosion resistance and machinability.
5. Zinc (Zn): When combined with aluminum and magnesium, it forms a strengthening phase, which increases tensile strength and yield strength.
6. Titanium (Ti) and Boron (B): Commonly used as grain refiners in aluminum alloys, improving the alloy’s microstructure.
7. Chromium (Cr): Added to certain aluminum alloys to form intermetallic compounds, improving the alloy’s strength and toughness.
These element additions play a vital role in defining the properties and applications of aluminum alloys, making them indispensable in a variety of industries.
Application of aluminum in jewelry manufacturing
The application of aluminum in jewelry manufacturing is relatively new, but it has shown great potential and room for innovation. Aluminum is light in weight, ductile and plastic, making it an ideal material for jewelry. Through anodizing and dyeing techniques, the surface of aluminum can present rich colors and textures to meet the diverse needs of modern jewelry design.
In addition, aluminum has a low melting point and is easy to process, which is conducive to the molding and mass production of jewelry. Jewelry supplier‘s environmentally friendly characteristics and cost-effectiveness provide a competitive advantage for the jewelry industry and also bring style and sustainability to the field of jewelry design.